From Full NDI® to NDI®|HX3: Understanding the Evolution.
Since the introduction of NDI®|HX there’s been ongoing curiosity about how it compares to the original NDI® Full Bandwidth that debuted in 2015. Adding to the mix, NDI®|HX2 emerged in 2019, and NDI®|HX3 further complicating the landscape. This article will break down the similarities and distinctions between these versions.
Introduction: Technology is Always Evolving, the MPEG-2 Analogy.
If you’re still curious, continue reading below for the full story and all the details.
NDI®: Revolutionizing Live Video Production.
The NDI® Core Advantage: Easy for Everybody.
Full NDI®: The Beginning.
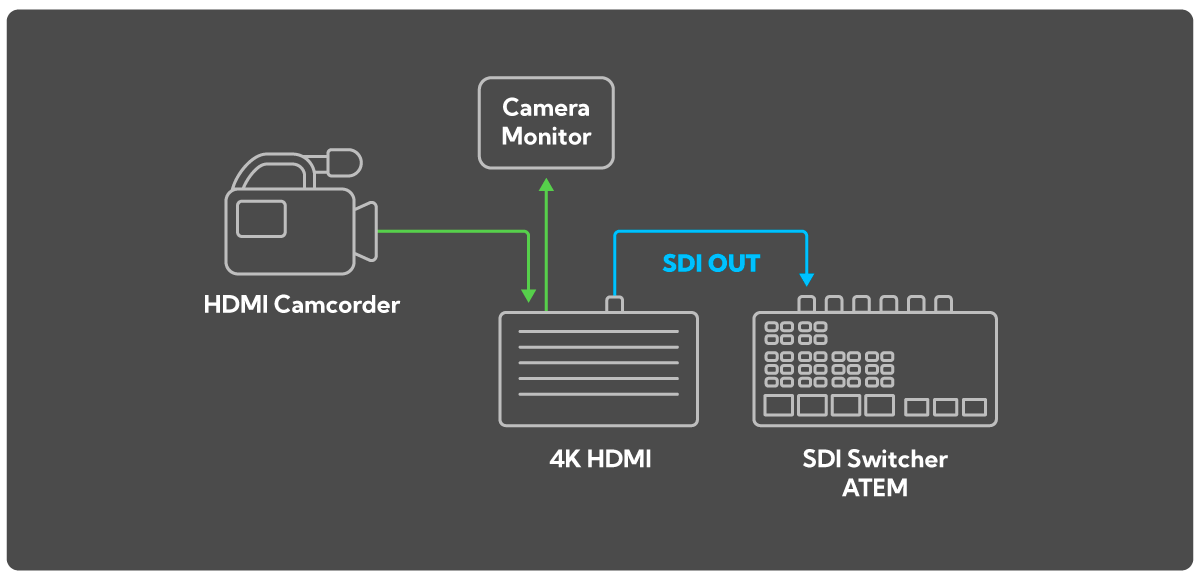
Expanding the Ecosystem: The Evolution of NDI® | HX.
NDI®|HX2: High Efficiency for Challenging Networks.
NDI®|HX3: The Best of Two Worlds.
NDI®|HX3 Certified: Ensuring Compatibility Across Devices.
NDI®|HX3: The Right Tool for Camera Applications.
NDI®|HX3: BirdDog Cameras Enable ALL Resolutions up to 4K60.
BirdDog’s Vision on Full NDI® & NDI®|HX3: Tailored Solutions for Diverse Needs.
Conclusion: The Future of Live Video Production.
4K60p: Video resolution for Ultra High Definition or 4K.
5G: Is the 5th generation mobile network. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks.
AV: Wider audiovisual industry whether corporate, education, medical, installation, …
Bandwidth: Amount of data that can be transferred from one point to another within a network
Broadcasting: Broadcasting Industry refers mostly about television channels, radio stations, cable, high end streaming and satellite platforms
H.264: H.264 or MPEG-4 AVC (Advanced Video Coding) is a video coding format for recording and distributing HD video and audio
H.265: High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as a successor to H.264
Latency: How much time it takes for a data packet to travel from one designated point to another.
LTE: Long-term Evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, also known as 4G.
MPEG2: A video encoding and compressing standard based mostly on motion vector estimation.
NDI: NDI is a network protocol that enables audio, video, and metadata signals to be sent over standard networks in real-time. NDI is bidirectional, low latency, and can transmit video up to 4K.
SpeedHQ: Compression codec based on MPEG2 developed by NewTek as part of NDI.
SRT: SRT is a video streaming transport protocol and technology stack designed to connect two endpoints to deliver low latency video and other media streams across any network including the public internet.
Resolution: Video resolution refers to the total number of pixels in a video frame rate. It dictates the amount of visual detail and sharpness in your video, and how crisp or blurry the image looks.